The spread is the difference between the buying price (bid) and the selling price (ask) of a currency pair. It is the cost of transacting a trade. The spread changes continuously depending on liquidity and market conditions and can range from a fraction of a pip to several pips. By understanding the spread, traders can capitalize on opportunities when they arise and know when the market is not worth entering.
It is important to understand exactly how the spread, a fundamental factor in the foreign exchange market, works. Spreads will vary depending on liquidity, volatility, and other market conditions. Generally, the more liquid a currency pair is, the narrower the spread will be, which means that the price difference between the bid and ask is smaller. Similarly, when volatility or market conditions pick up, spreads will generally widen, meaning the cost of trading goes up.
By understanding the spread, traders can identify when certain price movements or trends in the currency pair may be beneficial or costly. Knowing how much you can expect to pay in spread fees will help you determine which trades are the most beneficial to enter. Additionally, with the right strategies in place, traders can capitalize on opportunities when spreads narrow and avoid trades when spreads widen.
How to Calculate the Spread in Forex?
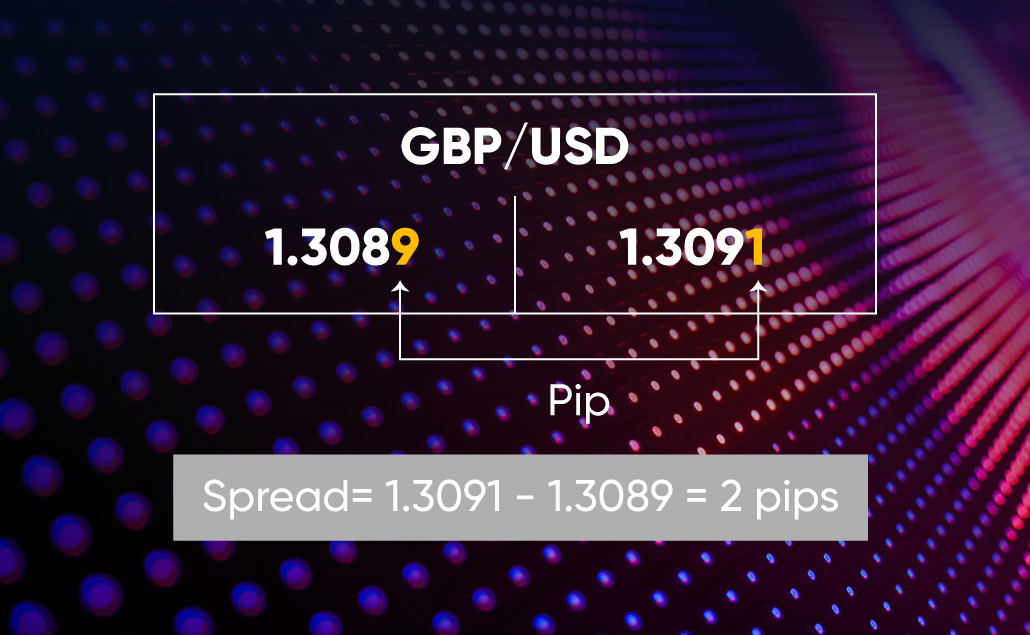
Spread in the Forex is typically measured in pips (1 pip = 0.0001) and is the broker’s commission for executing the trade. The formula for calculating the spread is:
Spread = Ask Price – Bid Price
For example, if the EUR/USD bid price is 1.3000 and the ask price is 1.3003, then the spread would be 3 pips (1.3003 – 1.3000 = 0.0003 = 3 pips).
What Determines the Spread in Forex?
The spread is determined by a variety of factors, but primarily by supply and demand. When a currency pair is in high demand, meaning many traders want to buy it, the bid price will be higher than the ask price and the spread will be larger. When demand is lower, the spread will be smaller. Spreads can also be affected by economic events, such as economic data releases, news events, and central bank decisions. Other factors affecting the spread include the liquidity of a currency pair, trading costs, and the broker’s markup. In some cases, a broker may add additional costs to the spread to make a profit.
At Eurotrader, we’re passionate about helping our members become successful traders. We provide an array of resources and support that make trading easier and more profitable. With our guidance, you can increase your return on investment and optimize your trading strategies. Join the Eurotrader community and start trading today to take your financial goals to the next level.
Related Articles
- What is a Currency Pair?
- What is Swap in Forex?
- What is Leverage in Forex?
- What is Pip in Forex?
- What is Margin in Trading?
Disclaimer
Eurotrader doesn’t represent that the material provided here is accurate, current, or complete, and therefore shouldn’t be relied upon as such. The information provided here, whether from a third party or not, isn’t to be considered as a recommendation; or an offer to buy or sell; or the solicitation of an offer to buy or sell any security, financial product, or instrument; or to participate in any particular trading strategy. We advise any readers of this content to seek their advice.