Arbitrage is a trading strategy that seeks to profit from price differences for the same asset across different markets. It works by buying an asset where it is cheaper and simultaneously selling it where it is more expensive, locking in the difference as profit.
Arbitrage opportunities arise when similar assets are traded on different markets and have different prices, resulting in a profit being made when the same asset is bought in one market and sold in the other. Arbitrage opportunities can also arise in the broader sense, involving the divergence of prices across different markets, as well as within a single market.
Arbitrage aims to take advantage of mispricings and make a quick profit for the trader; it is considered to be a low-risk but not risk-free strategy because, as long as the pricing differences exist, a trader can often make a profit, although transaction costs, exchange rates, and execution speed may impact results. For new traders learning how to trade arbitrage, it is crucial to understand both the opportunities and the risks.
Arbitrage is often viewed as an arbitrageur’s quickest way of making a profit since it is based on the speed of trading rather than on the fluctuations of the underlying asset’s market price.
An example of an arbitrage opportunity could be buying one share of a company in Europe for €65 and subsequently selling the same share in the United States for $75. In theory, this creates a profit opportunity, although in practice exchange rates, fees, and timing must also be considered.
The concept of arbitrage is further illustrated by a quick example; if a trader believes that a certain stock is undervalued in one market, he can buy a large quantity of such stock and then resell it in another market for a higher price. This transaction can be done extremely quickly and with minimal risk, as the trader is simply exploiting the discrepancy between two markets. The difference in price between the two markets is the arbitrage opportunity and the profit arises from the difference in the prices.
Arbitrage trading is a type of trading where traders take advantage of price discrepancies between two or more markets. It involves buying a security from one market and simultaneously selling it in another market at a higher price, thereby making a profit. Arbitrage trading requires speed, access to multiple markets, and, in modern contexts, often advanced technology or models and can be carried out in any market, including stocks, bonds, commodities, currencies, and even on a crypto trading platform.
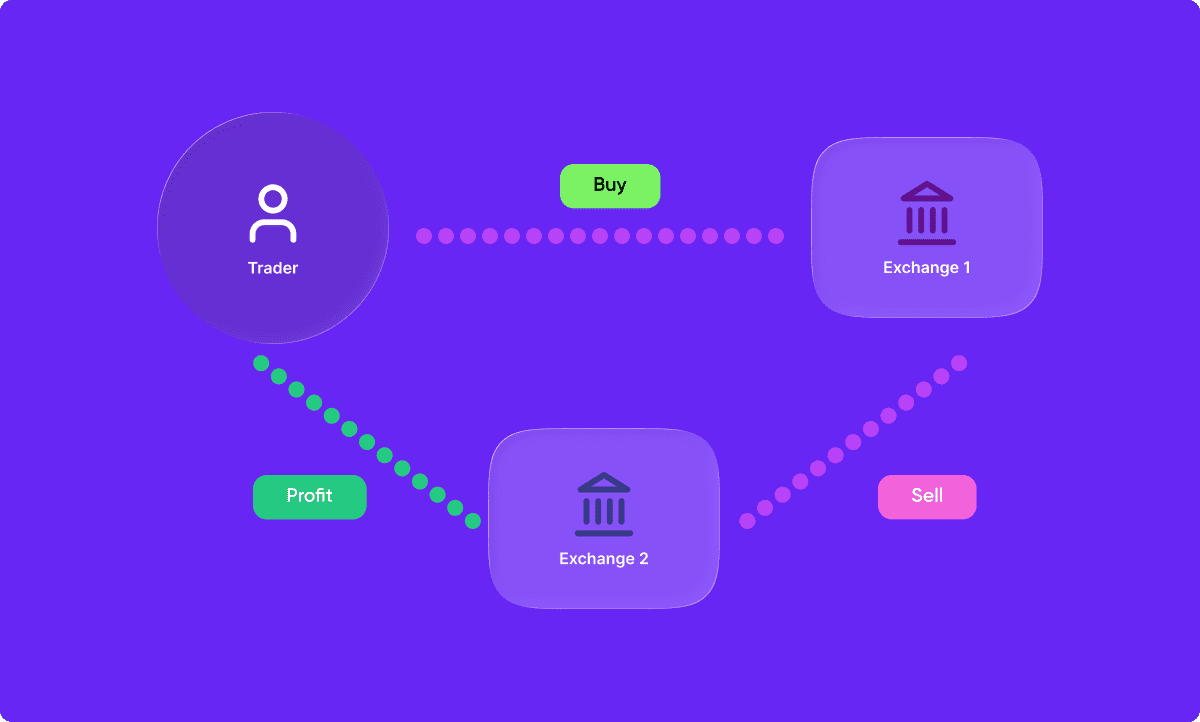
Arbitrage can occur in the same security on different markets, or across different securities on the same market. There are several different types of arbitrage that traders and investors can take advantage of.
While arbitrage is often called “low risk,” traders must account for:
At Eurotrader, we’re passionate about helping our members become successful traders. Our forex trading platform provides educational resources, risk management tools, and access to global markets to help traders make the most of opportunities like arbitrage. With our guidance, you can increase your return on investment and optimize your trading strategies. Join the Eurotrader community and start trading today to take your financial goals to the next level.